-
HR analytics is a data-driven approach that helps organizations analyze workforce data to improve decision making, performance, and business outcomes through measurable insights.
-
Companies can implement HR analytics by collecting structured HR data, analyzing it through centralized platforms like Mekari Talenta, and turning insights into strategic workforce actions.
HR divisions that aim to elevate their strategic role and overall performance will inevitably encounter the concept of HR analytics as organizations shift toward data-driven decision making.
In fact, organizations using HR analytics are 33% more likely to outperform competitors in engagement and retention, according to Gartner research, as cited by Vorecol, highlighting how data has become a critical driver of modern HR strategy.
As businesses grow more complex, HR is no longer limited to administrative tasks but is expected to provide measurable insights that support workforce planning and business outcomes
Understanding HR analytics becomes essential for companies that want to optimize talent management, improve productivity, and minimize risks through structured data analysis.
But what exactly is HR analytics and what functions does it serve? These topics will be discussed comprehensively in the following article.
What Is HR Analytics?
HR Analytics is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting human resources (HR) data to help companies make more accurate and strategic data-driven decisions related to workforce management.
HR Analytics is a data-driven approach to HR management that aims to:
- measure the effectiveness of HR policies and programs,
- identify patterns and trends in employee behavior, and
- predict future workforce needs and risks.
For example, with HR Analytics, companies can analyze why turnover is high in a particular division and find data-based solutions, not merely assumptions.
The world of HR continues to evolve over time. If in the past HR functions were limited to employee administration, today HR has expanded far beyond that.
HR divisions now hold various responsibilities that fundamentally relate to managing human resources.
One of the main reasons this is possible is the existence of HR analytics, since it is closely linked to organizational decision-making.
As previously explained, HR analytics, which may also be referred to as people analytics or talent analytics, is the process of collecting, analyzing, and reporting HR-related data.
In addition, this analytical process enables companies to measure the impact of various HR policies on overall business performance, allowing organizations to make decisions based on data.
In other words, HR analytics is a data-based approach to workforce management.
Data analysis allows HR practitioners to make informed decisions and test the effectiveness of the policies they have implemented.
It can also be said that HR analytics has similarities with people analytics, although the two have slight differences.
HR analytics measures HR department functions that relate to KPIs or key performance indicators.
Meanwhile, people analytics has a broader scope, ranging from measuring all HR-related information and employee data to reviewing insights from a business perspective.
Types of HR Analytics
HR Analytics can be grouped into four main types, explained based on analytical depth:
1. Descriptive Analytics
This type of analytics answers the question “what happened?”. Examples include quantitative reporting on last month’s average attendance rate, turnover numbers, or performance score distribution.
Descriptive Analytics is useful for providing a baseline overview and forming the foundation for deeper analysis.
2. Diagnostic Analytics
This focuses on analyzing the causes behind certain conditions. For example, why department X experiences an increase in absenteeism during specific seasons.
Using methods such as regression analysis or pivot tables, HR can investigate contributing factors (such as work stress, excessive overtime, or inadequate compensation) and take corrective action on the root causes.
3. Predictive Analytics
This type focuses on forecasting the future. For instance, whether employees with low satisfaction survey scores are at risk of resigning next year.
Companies can use machine learning to model trends and determine probabilities, allowing them to take retention actions before employees leave.
4. Prescriptive Analytics
This goes beyond prediction; HR Analytics can also recommend specific actions to take, such as offering development programs or bonuses for high-potential employees, or restructuring training schedules to maximize effectiveness.
Data Sources for HR Analytics
The effectiveness of HR analytics is closely tied to the variety and quality of data being analyzed.
To gain a comprehensive understanding of workforce trends, organizations typically gather information from multiple HR touchpoints across the employee lifecycle.
Common data sources include:
- Attendance and tardiness data: attendance frequency, lateness duration, and leave patterns.
- Turnover and retention data: resignation numbers, tenure duration, and exit reasons.
- Performance evaluation scores: appraisal results, KPIs, and promotion recommendations.
- Training cost and effectiveness: training expenses, attendance, and performance improvements after training.
- Recruitment data: hiring duration, recruitment channels, and performance per candidate source.
- Engagement survey results: satisfaction scores, motivational factors, and trust in management.
- Data generated from employee self-service (ESS) features: such as leave requests, attendance updates, or profile changes, which can reveal behavioral patterns over time.
The more complete and reliable the data collected, the more accurate and actionable the analytical outcomes will be.
In many organizations, these datasets are consolidated into an HR dashboard, enabling HR leaders to interpret patterns quickly without manually reviewing raw spreadsheets.
Objectives of Implementing HR Analytics
Human Resource Analytics (HR Analytics) has evolved into one of the most strategic approaches in modern HR management.
HR Analytics is not merely a collection of raw data, but a tool capable of transforming data into targeted decisions. Below are the main objectives of HR Analytics explained in detail:
1. Performance and Productivity Optimization
By using statistical data such as attendance frequency, workload distribution, and evaluation scores, HR teams can reassess the effectiveness of work processes.
HR Analytics enables the identification of high-performing teams or individuals as well as those who require intervention.
For example, if average productivity in department X declines by 15% during the last quarter, improvement actions — such as targeted training or workload redistribution — can be implemented immediately.
This system ensures that every operational aspect runs optimally, allowing organizations to grow based on data rather than assumptions.
2. Workforce Planning and Forecasting
Based on company growth trends, turnover rates, and expansion projections, HR Analytics can predict future workforce quantity and skill requirements.
If a company plans to open a new branch or launch an innovative product, the system can calculate the number of employees with specific competencies required, such as data analysts or digital marketing technicians.
HR analytics also supports employee lifecycle management by tracking data from recruitment, onboarding, development, to exit stages.
Such projections help prevent understaffing or overstaffing situations in the future.
3. Turnover Reduction and Employee Retention Improvement
Historical data analysis — including performance, job satisfaction, compensation, and tenure — helps identify patterns that lead employees to leave the company.
By understanding the main drivers behind resignations, HR can design effective retention strategies, such as career development programs, reward systems, or workplace culture improvements.
These preventive efforts reduce recruitment and replacement training costs.
4. Recruitment Effectiveness
HR Analytics enables organizations to measure recruitment success: how long the hiring process takes, where candidates come from, and how long they remain after joining.
Using this data, HR teams can optimize recruitment channels (job boards, internal referrals, campus recruitment, and more) and negotiate cost per hire (CPH).
For example, if candidates from platform A show higher retention rates, budget allocation can be increased for that platform.
5. Supporting Succession Planning and Career Development
By analyzing individual profiles — including performance reviews, potential assessments, and competency gaps — HR can prepare internal candidates to fill strategic positions.
HR Analytics provides an objective foundation to determine who should be promoted or developed through training programs, mentoring, or job rotation, ensuring organizational continuity.
6. Evaluation of Training or Incentive Programs
HR Analytics allows organizations to assess the effectiveness of training programs, whether in terms of knowledge improvement, performance enhancement, or error reduction.
Indicators that can be tracked include pre- and post-assessment results, task completion speed, and satisfaction surveys.
Based on these insights, HR can modify or replicate effective programs.
Benefits and Functions of HR Analytics
HR analytics has become a major focus for many companies because it transforms data into valuable insights that support organizational growth.
Here are several additional benefits:
1. Data-Driven Decision Making
HR analytics encourages organizations to make decisions based on data.
For example, HR analytics can analyze high turnover rates and help companies create new policies to reduce them through evidence-based insights.
2. Improving Organizational Performance
Another benefit is improving performance across all company divisions.
Organizations can analyze various factors, including employee workload, attendance, diversity and inclusion metrics, and workforce trends.
All of these insights can be used to optimize future decisions and enhance employee performance.
3. Enhancing Recruitment Systems
Companies can analyze employees who stay and those who resign, including their reasons for leaving, departments, and other factors.
Afterward, organizations can process the data and develop strategies to improve employee retention and recruitment quality.
4. Supporting Strategic Planning
HR divisions can contribute significantly to strategic planning.
This is achieved by translating HR data and reports into actionable plans that can be implemented within the workplace.
Insights generated from HR analytics help organizations refine their broader human capital management strategy.
HR Analytics Process in Companies
Turning raw HR data into strategic decisions requires a structured process. While every organization may approach analytics differently, the steps below outline a general framework that HR teams can follow when implementing HR analytics in practice.
1. Collect Relevant Data
The first step in any HR analytics initiative is identifying and gathering the right data. Organizations should define their primary objectives, whether improving performance, reducing turnover, or optimizing workforce planning, before deciding which datasets are needed.
Relevant data may come from attendance records, payroll systems, performance reviews, recruitment platforms, or employee engagement surveys.
Establishing a clear data framework early helps streamline analysis, reduce unnecessary work, and ensure that insights remain aligned with business goals.
2. Analyze Data Using Centralized HR Platforms
Once data has been collected, the next step is to transform it into meaningful insights. Many organizations rely on centralized systems such as HRIS, HRMS, or HCM platforms to organize data, automate reporting, and support deeper analysis.
An HRIS acts as a centralized hub for employee information, workflows, and reporting structures.
By integrating multiple HR functions into one platform, HR teams can analyze workforce trends more efficiently without relying on manual spreadsheets.
For example, platforms like Mekari Talenta provide HR analytics capabilities through features such as Talenta Insights, where HR teams can monitor headcount trends, attendance patterns, payroll data, employee performance, and even resignation risk predictions through visual dashboards.
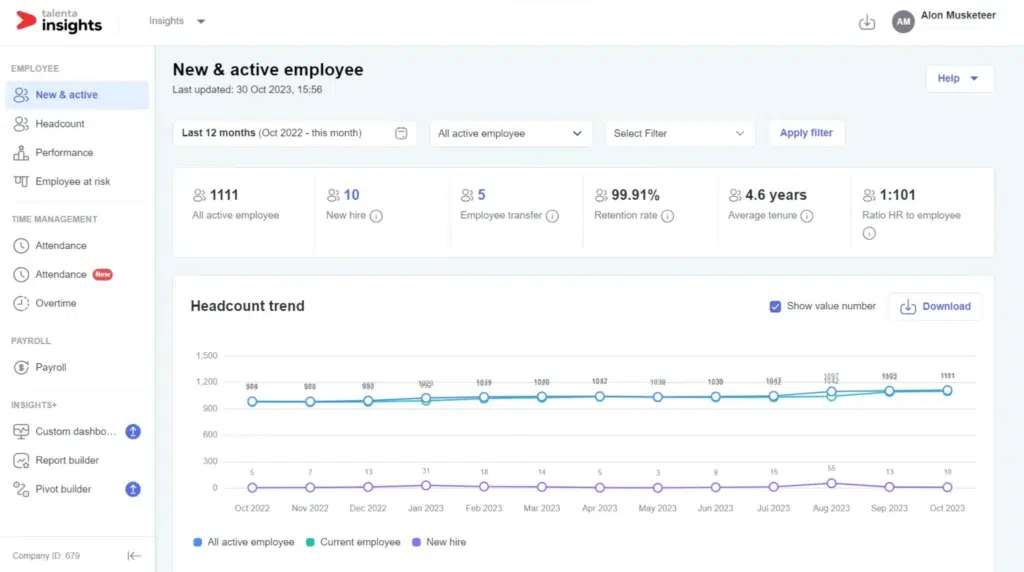
To learn more about this feature, please watch the following video.
Read also: HRIS vs HRMS vs HCM: What’s the Difference & What to Consider?
3. Translate Insights into Action Plans
After analysis is completed, the focus shifts to execution. HR teams need to interpret analytical findings and convert them into clear action plans, whether that means adjusting recruitment strategies, introducing targeted training programs, or improving employee engagement initiatives.
When decisions are guided by analytics rather than assumptions, organizations can implement changes more confidently and measure their impact over time.
4. Streamline Processes and Refine Data Frameworks
HR analytics can become complex if processes are not clearly structured. To maintain efficiency, organizations should continuously refine their data collection methods, remove irrelevant datasets, and simplify reporting workflows.
Using standardized dashboards or predefined analytics frameworks can reduce repetitive tasks and make future analysis more scalable.
Over time, this structured approach allows HR teams to focus more on strategic insights rather than manual data preparation.
5. Establish Data-Driven KPIs
Analytics becomes more impactful when tied to measurable outcomes. Organizations should define KPIs and ROI metrics based on reliable data, such as productivity trends, retention rates, overtime costs, or performance growth.
With tools like Talenta Insights dashboards, including Employee Performance, Turnover, Attendance, and Payroll views, HR teams can monitor KPI progress continuously and identify areas that require attention or improvement.
6. Leverage Technology to Scale HR Analytics
As HR data grows in volume and complexity, technology becomes essential for maintaining accuracy and scalability.
Many modern organizations adopt cloud-based HR platforms instead of traditional on-premise systems because they enable real-time access, centralized dashboards, and easier integration across HR functions.
Through this integrated ecosystem, data from payroll management, employee administration, and attendance management can be consolidated into a single analytics environment, allowing organizations to analyze workforce trends more holistically.
Within these platforms, features like customizable analytics views or custom dashboards help HR leaders tailor insights based on strategic priorities and monitor KPIs more effectively.
By integrating analytics into everyday HR operations, companies can move beyond reactive reporting and build a more proactive, data-driven HR strategy.
Read also: Cloud-based HRIS vs On-Premise: Key Differences and How to Choose
Examples of HR Analytics Implementation
Here are several implementation examples:
Case Study 1: Predicting Resignations Within 6 Months
An IT company uses machine learning based on job satisfaction and attendance data to predict resignation risk.
Result: turnover rates decreased by 25% after implementing insight-driven retention programs.
Case Study 2: Recruitment Optimization and Talent Pool Development
A retail company uses candidate conversion data from multiple channels and training effectiveness periods.
The most effective sources were allocated to three digital platforms, resulting in a 30% reduction in recruitment costs.
Challenges in Implementing HR Analytics
Despite its potential, HR Analytics faces several real challenges:
- Data Fragmentation: HR data is often spread across different applications (attendance, payroll, performance), making integration demanding.
- Limited Analytical Skills: HR teams need training in statistics, data visualization, and predictive modeling.
- Data Limitations: Attendance or turnover data may not be entered consistently or completely, affecting accuracy.
- Privacy and Security: Regulations such as GDPR or Indonesia’s Personal Data Protection Law (PDP) require explicit consent when using personal data for analysis.
Turn HR Analytics Into Real Business Decisions with Talenta Insights
Many organizations already collect large volumes of HR data, from attendance records and payroll expenses to performance reviews and employee lifecycle metrics.
However, when data is scattered across different systems, HR teams often struggle to turn information into clear strategic actions.
As businesses scale, challenges such as fragmented reporting, limited visibility, and data security risks can slow down decision making instead of supporting it.
An integrated HRIS platform like Mekari Talenta helps address these challenges by bringing HR operations and analytics into one connected ecosystem.
Mekari Talenta offers scalable HR analytics capabilities supported by cloud technology and an ISO 27001 certified security system.
As part of Mekari’s integrated software ecosystem, Talenta enables seamless connectivity across HR, finance, and business workflows, helping organizations streamline processes and maintain data consistency across systems.
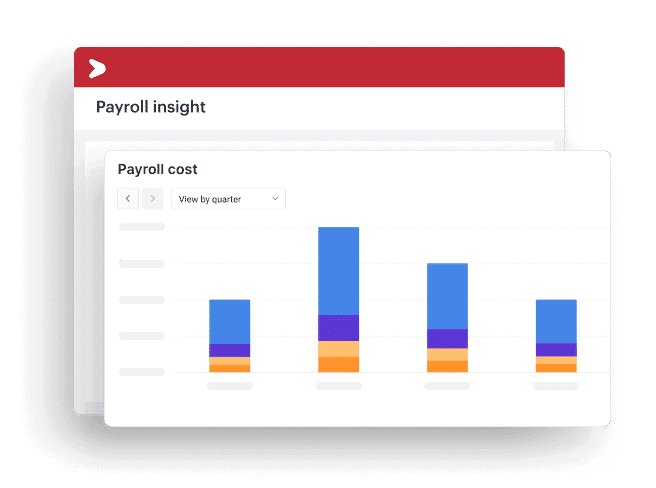
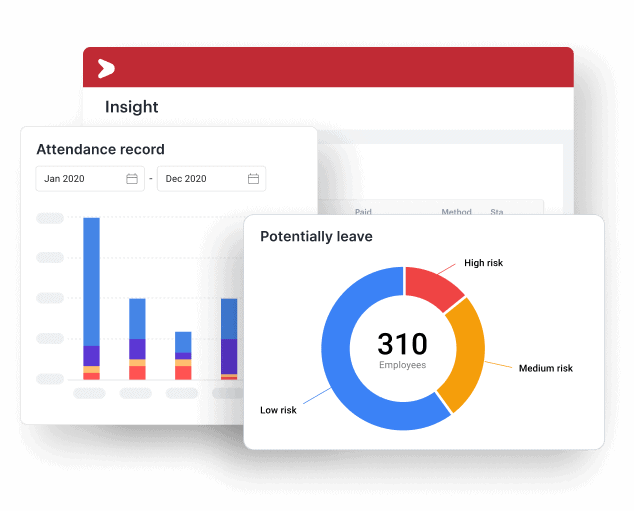
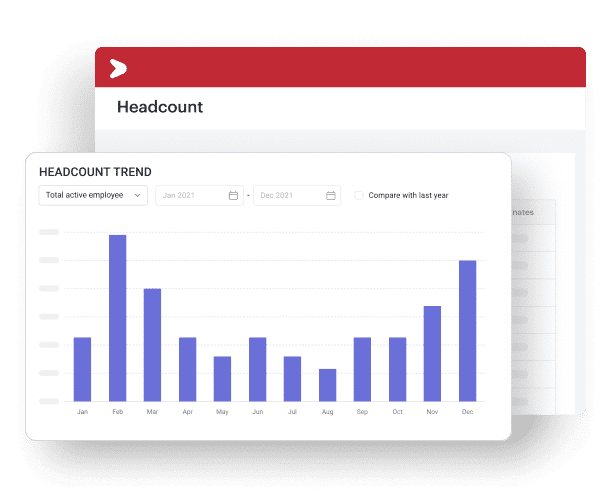
Through Talenta Insights, organizations can access a centralized HR dashboard designed to transform complex workforce data into actionable insights. Key capabilities include:
- Centralized HR dashboard that consolidates headcount, attendance, payroll, and employee performance data in one view
- Real time people analytics to monitor workforce trends, operational metrics, and HR expenditures
- Employee at Risk prediction to identify potential resignation risks based on behavioral patterns
- Custom dashboard and flexible reporting to support different business needs and organizational scalability
- Attendance, overtime, and payroll insights that help organizations control costs and improve operational efficiency
- On demand analytics with pre built and customizable reports for faster decision making
- Secure cloud based infrastructure with ISO 27001 certification to protect sensitive HR data
- Integration with payroll, employee management, and attendance systems for deeper cross functional analysis
By leveraging an integrated HR analytics platform, organizations can move beyond manual reporting and reactive decisions.
Talenta Insights helps HR leaders gain a clearer understanding of workforce dynamics, improve strategic planning, and build a more proactive data driven HR strategy aligned with business growth.
If you are ready to transform your HR analytics into strategic business insights, explore how Talenta Insights works through a free demo or connect with our team to discuss how Mekari Talenta can support your organization’s needs.




